Axaptapedia is now maintained by AgileCadence For more information please click here.
AOS networking
An understanding of AOS networking is useful to troubleshoot connection problems in an Axapta 3-tier environment.
Introduction[edit]
A brief technical description of the 3-tier architecture is useful as a starting point. See the Axapta AOS architecture article for more general information on 3-tier installations.
For the purposes of this article, we can look at the Axapta AOS as consisting of two discrete parts.
- AOS Manager (ax32mgr.exe)
- One or more individual AOS instances (ax32serv.exe)
The AOS manager is responsible for listening for client requests to the server and responding with information about available AOS instances. This information is transferred using port 2712/UDP. This port, along with 2712/TCP is [officially registered] for the Axapta Object Communications Protocol (AOCP).
Since Version 4 the communication between the AOS instance and the clients is made via RPC.
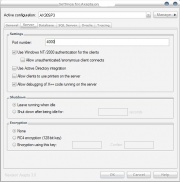
Each AOS instance listens on a port which is either randomly assigned by the AOS Manager or is set by the administrator in the AOS setup. See the image to the right for the port setup location.
Standard connection process[edit]
The standard connection process between an Axapta 3-tier client, and the AOS, is as follows:
- Client broadcasts on 2712/UDP requesting a response from the AOS Manager
- AOS Manager responds on 2712/UDP with details of the AOS instances available, including their port number and IP address
- Client contacts the AOS instance directly on the supplied IP address and port number (using TCP)
There are two situations where the standard connection procedure will prove troublesome
- UDP traffic is blocked due to a firewall
- The internal IP address of the server is not publically available to the clients
In these situations, it may be necessary for the clients to bypass the UDP broadcast/receipt and contact the AOS directly.
In Dynamics AX2009 the connection process depends on the server- and cluster configuration.
The client tries to connect to the AOS server instance, defined in the client-configuration. If the AOS server instance
is not responding, the clients tries the next one (if defined in the client-configuration).
If the AOS server nstance is a dedicated load balancer, the AOS gives the client the order to connect to the AOS with the less load. If the AOS server instance is not a dedicated load balancer, it depends on the cluster configuration.
- Standard (default) cluster is a non-load balanced cluster, so the client is connection to the AOS defined in his client-configuration (multiple AOSs defined >> in the given order)
- not the default cluster > each (cluster member)AOS server instance is working as a load balancer, so the client gets the order to which AOS he has connect to (like a dedicated load balancer)
Connecting directly[edit]
Connecting directly to the AOS instance requires knowing the public IP address (or name) of the server and the port on which the desired AOS instance is running. Therefore you must have manually specified a port number on the Configuration of the AOS instance.
If for example, the server is running at IP 192.168.1.1 on port 4000, then clients will need to add the following into the Advanced box at the bottom of the General tab of the Axapta Configuration Utility.
-aos=192.168.1.1:4000
This will bypass the AOS discovery mechanism.